Discover how hormones affect your libido and find practical tips for managing imbalances to enhance your sex drive. This is essential reading for both men and women.
Hormones are vital in regulating nearly every aspect of your health, including metabolism, mood, energy levels, and immune response. Among these important functions, they significantly influence your sex drive, making them a key factor in overall well-being. Whether you’re male or female, understanding how hormones affect your libido can help you recognize changes and take proactive measures to maintain a healthy and fulfilling sex life. In this guide, we’ll delve into the intricate relationship between hormones, their effects on sexual desire, and practical tips for naturally boosting your libido.
Research indicates that around 43% of women and 31% of men experience sexual dysfunction at some point in their lives. Hormonal imbalances often contribute significantly to these challenges. Hormones such as testosterone and estrogen have a major impact on sexual desire and overall libido. This article will examine how these hormones influence both men and women, the effects of stress and lifestyle choices, medical conditions, and natural methods to enhance sex drive.
Understanding Hormones and Their Role in Sexual Health
What are Hormone ?
Hormones are chemical messengers protein in nature produced by glands in your endocrine system and circulate in the bloodstream, playing a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions such as metabolism, mood, and sexual desire. These hormones are produced by glands like the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands, and gonads, and they significantly impact the sexual response cycle and overall libido.
What are the key hormones involved in sexual desire?
Several hormones are key players in influencing sex drive. Let’s explore the main hormones that regulate sexual desire.
Testosterone: The Driving Force
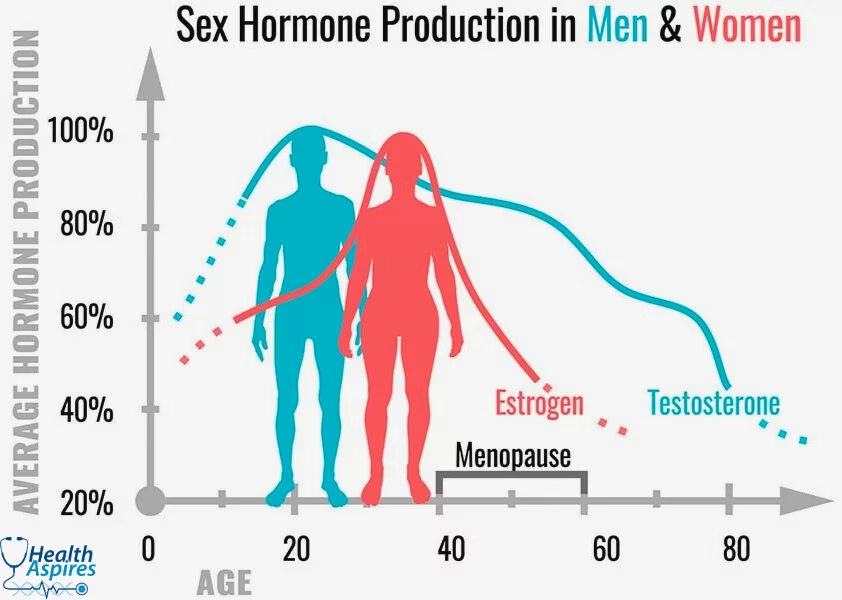
Testosterone, often referred to as the male sex hormone, is essential for libido in both men and women. In men, it is mainly produced in the testes, while in women, it is generated in the ovaries and adrenal glands. This hormone is a major driver of sexual desire and contributes to the development of secondary sexual characteristics, including muscle mass and body hair.
Studies show that men with lower testosterone levels often report reduced sex drive. For instance, a 2018 study found that men with testosterone levels below 300 ng/dL had a significantly lower libido compared to those with higher levels.
- In men, testosterone levels peak during adolescence and early adulthood, then gradually decline with age.
- Although women have lower testosterone levels, it still plays a significant role in their sex drive.
- Low testosterone can lead to decreased libido, challenges in achieving sexual arousal, and even erectile dysfunction in men.
Estrogen: The Feminine Connection
Estrogen is commonly linked to female sexual health, but it also influences men’s libido. In women, estrogen levels vary throughout the menstrual cycle, significantly affecting sexual desire. Higher estrogen levels, typically seen during ovulation, are associated with an increased sex drive, while lower levels, such as those experienced during menopause, can result in vaginal dryness and a decrease in libido.
In men, estrogen has a less recognized role in supporting sexual function, as it helps maintain the balance between testosterone and other hormones. When estrogen levels rise in men, it can lead to a reduction in testosterone and a subsequent decline in libido.
Progesterone: The Hormone of Balance
Progesterone, another important hormone for women, works in tandem with estrogen. At certain points in the menstrual cycle, elevated progesterone levels can suppress sexual desire. This hormone peaks during the luteal phase, after ovulation, which can result in lowered libido or a lack of interest in sex.
Men also have progesterone, but in much smaller quantities. Nevertheless, an imbalance—especially an excess—can lead to sexual dysfunction and decreased testosterone levels.
The Hormonal Cycle: Understanding How Hormones Fluctuate
Both men and women experience changes in hormone levels over time. Grasping these cycles and their connection to shifts in libido can shed light on sexual behavior.
- In Men: The Testosterone Cycle
- Men’s testosterone levels typically follow a daily pattern, peaking in the morning and gradually declining throughout the day. This circadian rhythm influences their overall libido, meaning men may feel a stronger sexual desire in the early hours compared to the evening.
- Statistic Suggestion: Research indicates that 40% of men notice a decrease in libido as their testosterone levels drop with age.
Moreover, aging significantly impacts men’s hormone levels. As men grow older, testosterone production naturally decreases, which can lead to lower sex drive and diminished sexual performance.
- In Women: The Menstrual Cycle’s Impact
- Women’s hormones fluctuate more noticeably due to their menstrual cycle, which can significantly affect their sexual desire. Estrogen levels peak around ovulation, boosting libido, while progesterone increases in the latter half of the cycle, sometimes resulting in a reduced interest in sex.
- Menstrual cycles can differ, but some studies suggest that women’s libido may vary by as much as 50% throughout the month due to hormonal shifts.
The Impact of Stress on Hormones and Sex Drive
The Stress-Hormone Connection
Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, can have a significant impact on libido. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to a decrease in testosterone, which in turn reduces sexual desire. For instance, someone in a high-stress job might experience fatigue and a lack of interest in sexual activities.
Managing Stress to Boost Libido
Effectively managing stress can greatly improve libido. Here are some practical strategies:
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps lower cortisol levels.
- Meditation: Mindfulness techniques can help soothe the mind.
- Therapy: Talking to a professional can help tackle emotional stress.
A study conducted in 2020 found that individuals who employed stress-reduction methods reported enhancements in both their mental well-being and sexual interest.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Hormones and Sex Drive
Nutrition and its Role
Diet is crucial for hormone production. Consuming foods rich in healthy fats, such as avocados and nuts, supports hormone health. Incorporating dark leafy greens, berries, and lean proteins can aid in stabilizing hormone levels.
Sleep and its Influence
Lack of sleep can disrupt hormonal balance. Insufficient sleep raises cortisol levels while lowering testosterone, which can adversely affect libido. Striving for 7-9 hours of quality sleep is vital for sustaining sexual health.
Medical Conditions Affecting Hormones and Sex Drive
Common Medical Conditions
Medical issues like diabetes and thyroid disorders can interfere with hormone levels and impact sex drive. Additionally, mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety are significant factors, with research showing that almost 75% of people dealing with depression report a decrease in libido.
Seeking Professional Help
It’s crucial for individuals experiencing significant libido problems to seek advice from healthcare professionals. They may suggest tests to evaluate hormone levels and explore treatment options, which could involve hormone therapy or other medications.
Hormonal Changes Across Life Stages
Puberty and the Onset of Sexual Desire
During puberty, hormonal changes play a crucial role in developing sexual characteristics and igniting sexual desire. Both men and women experience a surge in testosterone during this time, which contributes to an increased interest in sexual activities.
The Mid-Life Shift: Andropause and Menopause
As people grow older, they may undergo hormonal changes that impact their libido. For men, andropause is a condition marked by a decrease in testosterone levels, which can lead to diminished sexual desire, energy, and performance. Women, on the other hand, go through menopause, signaling the end of their reproductive years, accompanied by a drop in estrogen and progesterone levels, often resulting in a decreased libido.
Research indicates that 25% of women experience a notable decline in sexual desire after menopause due to hormonal changes.
Natural Ways to Boost Libido
There are many natural ways to boost libido, including:
- Exercise: Regular exercise can enhance blood circulation, elevate mood, and increase libido.
- Maintain a healthy diet: A well-balanced diet can support hormonal balance, improve blood flow, and boost energy levels. Foods high in zinc, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins E and B can be beneficial for libido.
- Manage stress: High stress levels can negatively impact sex drive. Consider journaling, practicing meditation, or exploring other stress-relief techniques.
- Prioritize sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for regulating hormone levels.
- Enhance communication: Being open and honest with your partner can strengthen your emotional bond.
- Explore aphrodisiacs: Certain foods, herbs, and supplements are thought to act as natural aphrodisiacs, including:
- Oysters: Packed with zinc, which may elevate testosterone levels
- Saffron: A spice that could aid in reducing stress, improving mood, and supporting erectile function
- Maca root: An ancient herb rich in minerals like zinc, iodine, and essential fatty acids
- Engage in yoga or mindfulness: These practices might enhance sexual function
- Consider acupuncture: This alternative therapy may help boost libido
Hormone Therapy and Its Role in Restoring Libido
What Is Hormone Therapy?
Hormone therapy refers to the use of hormones or treatments that modify hormone levels to address imbalances or deficiencies in the body. It is often employed to tackle health concerns such as menopause, andropause, thyroid issues, and hormonal deficiencies resulting from medical conditions or aging. The therapy usually involves administering hormones like estrogen, testosterone, progesterone, or others, tailored to individual requirements.
Hormone therapy can be administered through several methods, including:
- Pills
- Patches
- Gels or creams
- Injections
- Implants
These methods assist in regulating hormone levels in the body, promoting balance and alleviating associated symptoms.
How Hormone Therapy Improves Libido
Addressing Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone are essential for sexual desire and function. When these hormones become imbalanced—often due to aging, menopause, or other health issues—it can lead to a decrease in libido. Hormone therapy aims to restore these hormones to their optimal levels, thereby enhancing sexual desire.
- Testosterone Replacement: Testosterone is a crucial hormone for both men and women that significantly affects libido. As men age, their testosterone levels may decline, leading to reduced sexual interest. Testosterone therapy has been proven to effectively boost libido in those with low testosterone levels.
- Estrogen Therapy: For women, decreasing estrogen levels during menopause can result in vaginal dryness and discomfort during sex, which can negatively affect libido. Estrogen therapy can help alleviate these issues, making intimacy more comfortable and enjoyable.
Enhancing Mood and Energy Levels:
Hormonal imbalances can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, mood swings, anxiety, and depression, all of which can adversely affect libido. By correcting these imbalances, hormone therapy can enhance overall well-being, which in turn can boost sexual desire.
Restoring Physical Health:
Hormonal decline can lead to issues like reduced muscle mass, increased fat accumulation, and decreased stamina, all of which can contribute to low libido. Hormone therapy can help reverse these physical changes, promoting a healthier body and renewed confidence, which can enhance sexual interest.
Improving Blood Flow and Sensitivity:
Hormones like estrogen and testosterone play a role in enhancing blood flow and sensitivity in sexual organs. For instance:
- In men, testosterone therapy can improve erectile function by promoting better vascular health.
In women, estrogen therapy increases blood flow to the genital area, enhancing arousal and sensation.
Hormones play a vital role in sexual desire for both men and women. From puberty to menopause or andropause, changes in hormone levels can significantly affect libido and sexual satisfaction. However, it’s important to recognize that hormones are only one aspect of the equation; psychological, emotional, and lifestyle factors also contribute to sexual well-being. By understanding the complexities of hormonal cycles and seeking professional guidance when needed, individuals can achieve healthier sexual lives at any stage.


