What is ALT (S.G.P.T) blood test ?
The enzyme known as alanine aminotransferase, or ALT (AL-uh-neen uh-mee-no-TRANS-fur-ace), aids the liver in converting food into energy. When the liver cells are injured the enzyme leak into blood so the Elevated enzyme levels may indicate hepatic injury or irritation, causing the enzymes to leak out of the liver cells.
ALT is occasionally referred to as an SGPT test because it was formerly known as serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, or SGPT. Liver play an important role in the in body so tracking liver health is important.
Table of Contents
What are the function of liver?
Liver’s Role in Health Maintenance
- Metabolism: Breaks down proteins, lipids, and carbs; controls blood sugar levels.
- Detoxification: Clears the bloodstream of alcohol, narcotics, and poisons.
- Storage: Holds iron, glycogen for energy, and vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12.
- Bile Production: This process creates bile to help break down and absorb lipids and fat-soluble vitamins.
- Protein Synthesis: Generates vital proteins such as clotting factors (for blood coagulation) and albumin (for blood volume maintenance).
- Immune Support: Contains Kupffer cells, which help the body fight off infections by eliminating them.
- Hormonal Regulation: Degrades and controls hormones like estrogen and insulin.
- Regulation of Cholesterol: produces, degrades, and eliminates cholesterol in bile.
- Ammonia Conversion: Produces urea, which is eliminated through urine, from harmful ammonia.
- Blood filtration: keeps circulation healthy by removing aging or damaged red blood cells.
What are the causes of liver damage?
- Drinking too much alcohol can cause cirrhosis and alcoholic liver disease.
- Viral Infections: Chronic liver damage can result from Hepatitis B and C.
- High cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity are frequently associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Overuse of drugs, such as acetaminophen, or exposure to toxic substances can result in drug and toxin overload.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Liver cells are attacked by diseases (Antigen) such as autoimmune hepatitis.
- Hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease are examples of genetic conditions.
- Chronic diseases include conditions such as metabolic syndrome and diabetes.
When need to test your ALT (SGPT)
Even if your doctor has no particular cause to be concerned, the ALT test can be performed as part of routine blood tests. Your doctor can use the ALT test to assess the effectiveness of your treatment if you have previously been diagnosed with liver disease. You need to visit laboratory to check your alt when you have the following condition.
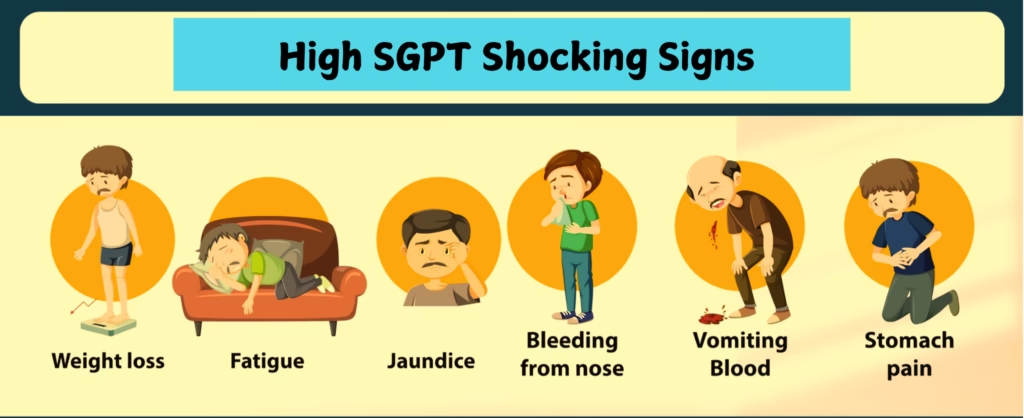
- Stomach pain or swelling
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- jaundice (Yellow skin or eyes)
- Weakness
- Extreme tiredness
- Dark-colored urine
- Light-colored poop
- Itchy skin
A doctor recommend ALT both for diagnosis and prognosis. If you found with a high ALT (S.G.P.T) and have some pathological sing and symptoms then you may have one the following condition.
- You are come into contact with a hepatitis virus.
- You are a heavy drinker.
- You have familial history of liver illness.
- You take medications that are known to harm the liver. These consist of analgesics like ibuprofen and acetaminophen
- You are obese
- you are diabetic
What is the normal ranges of ALT (SGPT) in human?
Normal ALT Ranges by Gender:
- Males: 10–40 U/L (units per liter)
- Females: 7–35 U/L
(Males typically have higher ALT levels due to larger liver size and different muscle mass.)
Normal ALT Ranges by Age:
Children:
- Newborns (<1 year): 13–45 U/L (higher due to liver immaturity)
- Children (1–12 years): 10–30 U/L
Adolescents (13–18 years):
- ALT levels may slightly increase, similar to adult levels, during growth spurts.
Adults (19–60 years):
- Males: 10–40 U/L
- Females: 7–35 U/L
Older Adults (>60 years):
ALT levels may decrease slightly with age due to reduced liver mass and physiological changes.
- Males: 10–35 U/L
- Females: 7–30 U/L
Which factors increase ALT Levels?
1. Dietary and lifestyle factors
Intense Exercise: Because it puts stress on the muscles, intense exercise might momentarily raise ALT levels.
High-Fat Diet: Eating a lot of fat can raise your ALT levels, especially if you’re also obese.
Alcohol Use: Alcohol consumption, even in little doses, might momentarily raise ALT levels.
Herbal Supplements: Some supplements, such as kava, valerian, or Echinacea, may raise ALT levels.
2. Over-the-Counter Pharmaceuticals: ALT can be raised by excessive use of acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen.
Prescription drugs: ALT levels may rise as a side effect of statins, antibiotics, anticonvulsants, or ant tuberculosis medications.
3. Physiological Conditions
Pregnancy: Because of physiological changes, ALT levels may rise during pregnancy.
Menstrual Cycle: Some women may have slightly elevated ALT levels due to hormonal changes during menstruation.
4. Metabolic Factors and Obesity
Obesity: Even in the absence of liver illness, excess body fat can cause slight elevations in ALT levels.
Because it puts stress on the liver cells, insulin resistance, which is common in metabolic syndrome, can raise ALT.
5. Other Factors
Dehydration: Liver enzyme levels may briefly rise as a result of severe dehydration.
Age and Gender: Young guys often have slightly greater ALT levels than females and older people.
Smoking: High ALT levels have been associated with long-term smoking.
Altitude: Because of hypoxic stress, living or exercising at high elevations might occasionally raise ALT level.
ALT Blood Test Preparation
There is no need to stop eating before test but better to stop stay fast some hours before test. That is because the ALT blood test is often done with other blood tests that require fasting.
Cretan medication and Intense exercise effects the result of your ALT so it is important to inform your doctor about any drugs or supplement you take. Also tell your doctor if you plan a vigorous workout before the test.
